
|
|
IMPLICIT COST: An opportunity cost that does NOT involve a money payment or a market transaction. This should be contrasted with explicit cost that DOES involve a money payment or a market transaction. The common misconception among non-economists out there in the real world is that the term "cost" is synonymous with the term "payment," that is, all costs are explicit costs, to be a cost you have to give up some money. Well, I'm here to tell you that this isn't true. Cost is opportunity cost. It's the satisfaction NOT received from activities NOT pursued. It's the value of foregone production. And not all opportunity costs involve a money payment.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           NUMBER OF SELLERS, SUPPLY DETERMINANT: The number of sellers willing and able to sell a good, which is assumed constant when a supply curve is constructed. The number of sellers is one of five supply determinants that shift the supply curve when they change. The other four are resource prices, production technology, other prices, and sellers' expectations. The number of sellers willing and able to buy a good affects the overall supply. The relation is relatively straightforward. With more sellers, there is more supply. With fewer sellers, there is less supply.All in the NumbersThe overall market supply of a good is based on the combination of supplies offered by each seller. If five firms are each willing and able to sell 100 units of a good, at the going market price, then the total market supply is 500 units. If a sixth firm should enter the market, also willing and able to sell 100 units, then the total market supply increases to 600 units. If one of the five original firms should leave the market, then the total market supply decreases to 400 units. With more sellers, there is a greater supply. With fewer sellers, there is less supply.Shifting the Supply Curve| Number of Sellers | 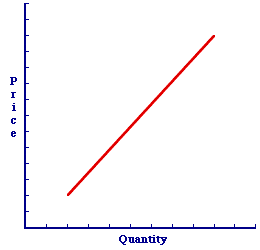 |
A change in number of sellers causes the supply curve to shift. This can be illustrated using the positively-sloped supply curve for Wacky Willy Stuffed Amigos presented in this exhibit. This supply curve captures the specific one-to-one, law of supply relation between supply price and quantity supplied. The number of sellers is assumed to remain constant with the construction of this supply curve.Now, consider how a change in the number of sellers shifts the supply curve. - More Sellers: If there is an increase in the number of sellers in the market, then the supply of the good increases. It is just that simple. This is seen as a rightward shift of the supply curve. Click the [More Sellers] button to demonstrate.
- Fewer Sellers: If there is a decrease in the number of sellers in the market, then the supply of the good decreases. Which is also straightforward. This is seen as a leftward shift of the supply curve. Click the [Fewer Sellers] button to demonstrate.
The Competition of NumbersThe number of participants on the selling side of the market is extremely important when it comes to competition and market control. Market control depends on the number of competitors. Fewer competitors means more market control for each. More competitors means less market control for each. A given seller, in general, would rather have fewer participants on the selling side, which would then give it greater market control. Good for the seller. Of course, fewer competitors and greater market control also means less efficiency. Bad for the economy.

Recommended Citation:NUMBER OF SELLERS, SUPPLY DETERMINANT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: April 29, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
BEIGE MUNDORTLE
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time watching infomercials seeking to buy either a decorative windchime with plastic or a flower arrangement for that special day for your mother. Be on the lookout for malfunctioning pocket calculators.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
A thousand years before metal coins were developed, clay tablet "checks" were used as money by the Babylonians.
|

|
|
"Something in human nature causes us to start slacking off at our moment of greatest accomplishment. As you become successful, you will need a great deal of self-discipline not to lose your sense of balance, humility and commitment." -- H. Ross Perot
|

|
JPAM
Journal of Policy Analysis and Management
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


